Work with database connection and repository
In this chapter, you will learn to configure database connection in workflows and processes and also to integrate Process Studio repository with source code control systems, such as Git and SVN. If you need to get or send data to or from a database, you can do so by configuring a database connection in your workflow or process. There are steps or entries that can enable you to set the connection.
The chapter consists of the following topics:
Create a database connection
You can configure database connection through Process Studio.
File menu
You have the option of configuring database connection through the File menu.
To configure a database connection:
- Click File and select New. The sub-menu appears.
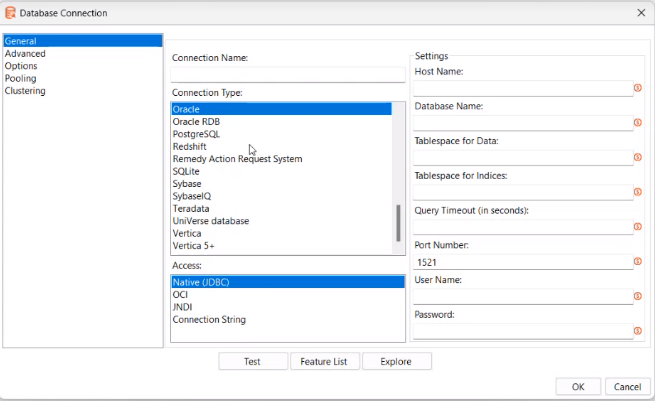
- In the sub-menu, select Database Connection. The Database Connection dialog appears.
Figure 66: Database Connection dialog
You can also configure database connection in the following ways:
- Go to Tools 🡪 Wizard 🡪 Create Database Connection... or F3.
- In the View tab:
- Select Database Connection and right-click. In the contextual menu, select New or New Connection Wizard
- Select existing database and right-click. In the contextual menu, select New.
- In addition, use other menu options in the following ways: Edit to modify the database connection details. Duplicate to duplicate the existing database connection. Copy to clipboard to copy the existing database connection. Delete to remove the selected database connection from the project.
-
In the first pane, select the connection you want, that is, General or Advanced or Options or Pooling, or Clustering. The fields in the second and third pane of the dialog change depending on the connection selected.
-
Enter or select the details in the fields, as required.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
| Connection Name | Enter a name for the database connection. |
| Connection Type | Select the type of connection you want for the database. For example, PostgreSQL. |
| Access | Select the type of access you want for the database. Available options are: |
| - Native (JDBC) | |
| - OCI | |
| - JNDI | |
| - Connection String | |
The availability of options depends on the type of connection selected. For example, when you select Connection String, the Connection String dialog appears. 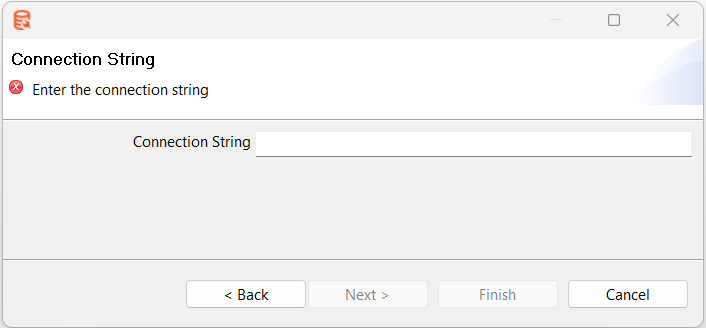 Enter the connection string and click Finish. Enter the connection string and click Finish. | |
| Settings | Enter the field details, as required. |
| - The fields available under Settings change depending on the type of connection and access selected. | |
| - The Query Timeout (in seconds) field is available only if you select Native (JDBC) or Connection String access option. |
-
Click Test to verify that the database connection is complete.
-
Click Feature List to view the list of features.
-
Click Explore to view the components, such as tables and views, of the selected database.
It may be possible to read from unsupported databases by using the generic database driver through JDBC connection. Contact AutomationEdge if you want to access a database type that is not yet in the list of supported components.
Connections
You can also configure shared database connections through Connections available in the Project Explorer.
Connections hold the project-level shared database connections. The shared database connections can be used across the workflows and processes under the selected project.
Configure new shared database
You can configure new shared database connections using any one of the following ways:
- In the Project Explorer, select Project 🡪 New 🡪 Database Connection
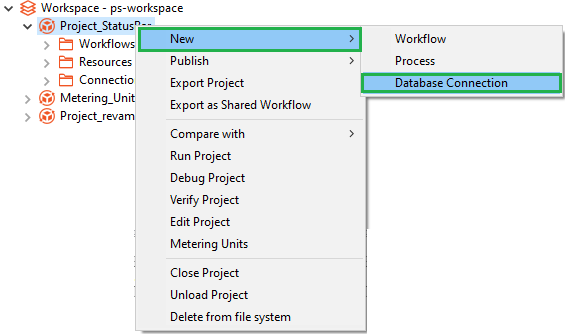
Figure 67: Project 🡪 New 🡪 Database Connection
OR
- In the Project Explorer, select Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Right click on Connections 🡪 New Database Connection
Figure 68: Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connection 🡪 New Database Connection
OR
- In the Project Explorer, select Workspace -> Project -> Connections -> Right click on Database connection -> New Database Connection
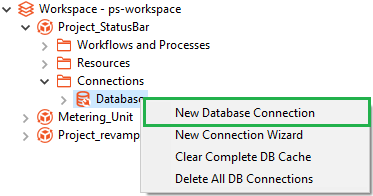
Figure 69: Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections 🡪 Database 🡪 New Database Connection
OR
- In the Project Explorer, select Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections 🡪 Database 🡪 Right click on database connection 🡪 New
Figure 70: Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections 🡪 Database 🡪 Database connection 🡪 New
For details about configuring the database connection, see File menu
Edit shared database connection
To edit a shared database connection, in the Project Explorer go to Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections 🡪 Database 🡪 select database connection, and right click on the connection. In the contextual menu, select Edit and modify the details.
Updating or modifying the database connection will also update the shared database in all workflows and processes.
Delete shared database connection
To delete a shared database connection, in the Project Explorer go to Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections, and right click on database. In the contextual menu, select Delete all DB Connections.
Updating or modifying the database connection will also update the shared database in all workflows and processes.
Share a local database connection
To share a local database connection, right click on local connection -> Share.
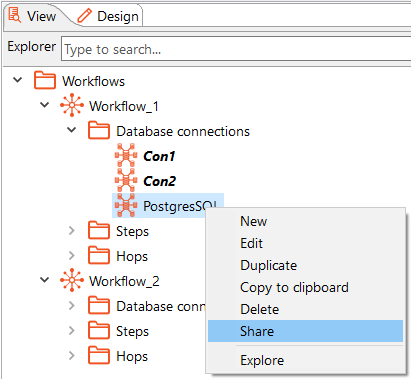
Figure 71: Workspace 🡪 Project 🡪 Connections 🡪 Database connection 🡪Database 🡪 Share
If you duplicate a local connection and make it shared database connection, then the shared database connection overrides across the connection in workflows and processes in the project.
Link a repository to Git and SVN
Integrate Process Studio with source code control systems, such as Git and SVN. You can create and link to multiple repositories and maintain process and workflow versions.
Prerequisites
-
For Git, initialize and update an online or local repository.
-
For SVN, initialize a local or remote repository. There are additional prerequisites for SVN, such as
- SlikSVN on Windows:
-
Download SlikSVN Windows Command Line Client,Slik-Subversion-1.9.7-x64 from (https://sliksvn.com/download/ or https://sliksvn.com/pub/) and install it.
-
Fetch a library file and copy C:\Program Files\SlikSvn\bin\libsvnjavahl-1.dll to Process Studio path libswt\win64 (64-bit) or to libswt\win32 (32-bit).
- SlikSVN on Linux (Debian or Ubuntu):
-
$ sudo apt-get install libsvn-java
-
Append /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/jni/ to LIBPATH in process-studio.sh as follows:
LIBPATH=$LIBPATH:/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/jni/
export LIBPATH
For more information on how to install libsvn-java 1.9.X on Ubuntu 14.04, see < https://tecadmin.net/install-subversion-1-9-on-ubuntu/>.
To link a repository to Git and SVN:
- Click View, and select Perspectives, the sub-menu appears.
You also select the perspective options using,
-
Select Git/SVN. If no repository is linked yet, a message asking for adding a repository appears.
-
Select Yes, and the Add Repository dialog appears.
Figure 72: Add Repository dialog
- Enter the details.
| Field name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Enter a name of the repository. |
| Description | Enter a description of the repository. |
| Directory | Select the directory path where the local Git or SVN repository to be linked is present. |
| Type | Select the type of linking you want, that is, Git or SVN. |
If the repository is already linked then you can directly view the operations performed on the repository.
- After linking the repository, a confirmation dialog appears. Click Yes, and you can view the operations performed on the repository.
Perspective toolbar
This section explains the tools used in the Git or SVN perspectives.
When performing actions, such as Push you will need to enter credentials. Click to view the password.
| Toolbar icon | Description |
|---|---|
| Use to add, open, edit, clone, or remove a project. Following options are available: | |
| - Open | |
| - Add | |
| - Remove | |
| - Edit | |
| - Clone | |
| Use to provide the path of the remote repository. The name of the remote repository should be origin. | |
| Use to sync the opened, local, and remote repository, and is equivalent to git pull. | |
| - In SVN, use Update instead of Pull. | |
| - The behavior of this tool varies depending on the configuration of origin and branches. | |
| Use to sync the opened, local, and remote repository, and is equivalent to git push. | |
| - In SVN, the option is unavailable | |
| - In Git, the behavior of this tool varies depending on the configuration of origin and branches. | |
| Use to checkout, create, delete, merge, and push branches. | |
| - Checkout: switch between branches. - Create: create a new branch. | |
| - Merge: merge multiple branches. Following are the options for merging: | |
| - Recursive | |
| - Ours | |
| - Theirs | |
| For a Git repository, files are saved as .ours or .theirs. | |
| For SVN repository, files are saved as .mine, .rXX, and .rYY. | |
| If there are conflicts when you merge the branches, you can resolve them by selecting the file in Changed files, and then selecting Stage. Commit these changes. To abort the merge, select Discard changes. | |
| - Delete: delete a branch. | |
| - Push: push a branch to origin or remote repository. | |
| Use to tag the branches. The functionalities are same as that of Branch. Merge option is unavailable. | |
| Use to refresh the view. |
Changed files
In this section, you can work on the files in the repository.
You can view the new or modified files in the Changed files pane. A
new file added to the repository has
icon against it. A modified file has
and removed file has
icons against it, respectively.
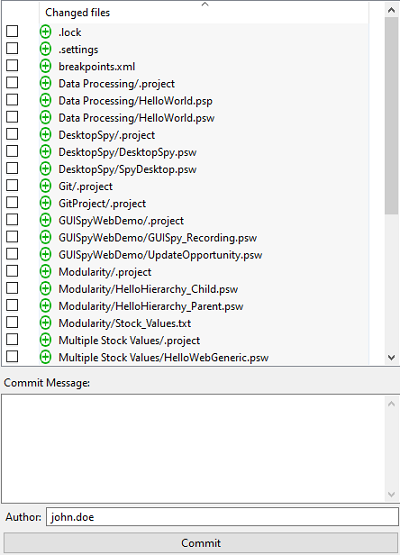
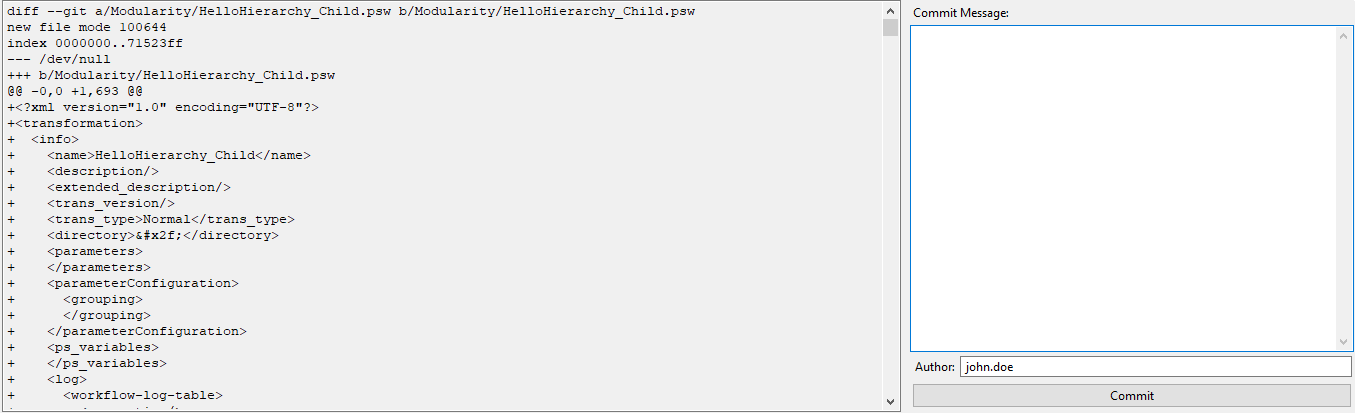
Figure 73: Add Repository dialog
To commit a file:
- In the Changed files pane, select the checkbox against the files that you want to commit.
- Select the file to view its details in the stage pane, then enter a comment in Commit Message.
Figure 74: Stage pane view
- Click Commit. The changes are committed to the working branch.
In the SVN perspective, committing the file pushes the updates to the remote repository.
- In Git perspective, click Push, to commit the updated branch to the repository. The changes are now available in the remote repository.